Understanding SCFAs: Types and Production
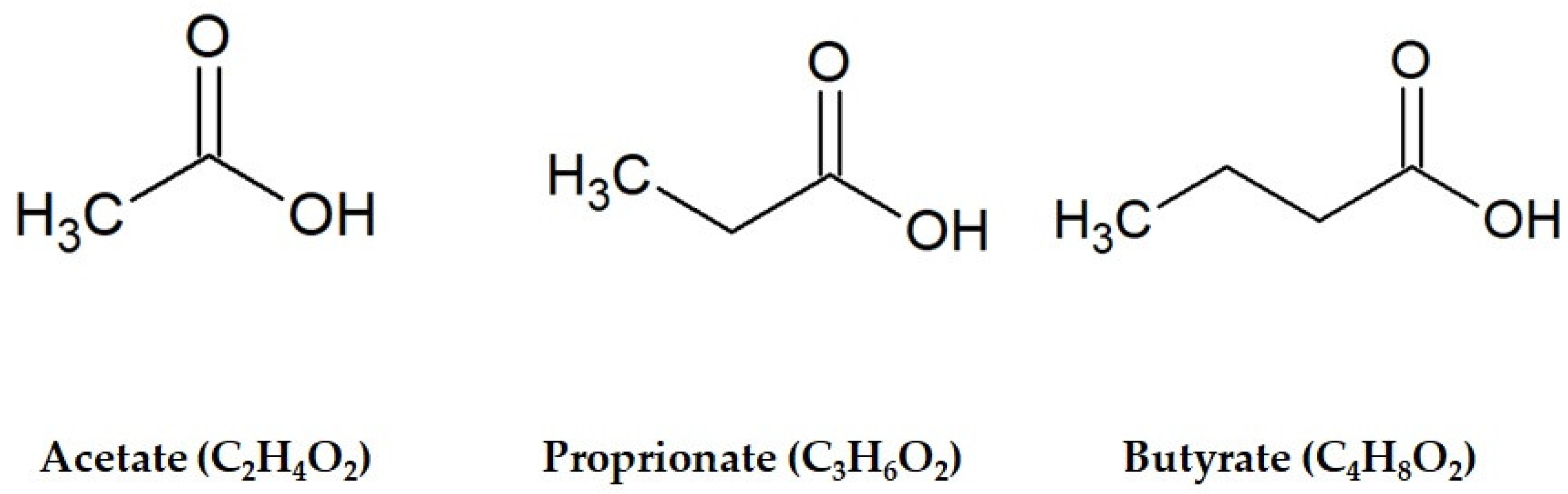
Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) are vital fats created in the large intestine when good bacteria break down fiber from the food we eat. These include acetate, propionate, and butyrate. SCFAs are essential for gut health, influencing various physiological processes like gut barrier function and inflammation modulation. Butyrate, in particular, is crucial as it provides energy to the cells lining the gut.
The production of SCFAs occurs through the fermentation of dietary fibers and resistant starches by beneficial gut bacteria, mainly Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. Foods rich in soluble fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and fermented foods, promote SCFA production. These fatty acids are not just digestion byproducts; they play key roles in managing gut health and overall well-being, impacting conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).
The Key benefits of Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
SCFAs offers a range of health benefits, crucial for maintaining gut health and beyond:
- Gut Health: Butyrate, in particular, is essential for the cells lining the intestine, promoting their health and integrity.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: SCFAs have the ability to reduce inflammation, not just in the gut but throughout the body.
- Blood Sugar and Appetite Regulation: Propionate plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar and appetite.
- Cholesterol Regulation: SCFAs contribute to reducing cholesterol synthesis in the liver.
Significance of SCFAs for Gut Health
In gut health in particular, SCFAs have very specific roles that are beneficial to a healthy gut.

1. Energy Source for Intestinal Cells: Butyrate serves as the main energy source for intestinal cells, ensuring their optimal function and maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier.
2. Maintenance of Gut Barrier Function: SCFAs, especially butyrate, strengthen the gut barrier function, enhancing the production of tight junction proteins. Tight junctions are like seals between cells that prevent substances from leaking between them.
3. Anti-inflammatory Properties: SCFAs possess anti-inflammatory properties, crucial for reducing inflammation in the gut and maintaining homeostasis (the process by which the organ maintains a stable environment despite changes in the external conditions).
4. Regulation of Gut Motility: SCFAs influence gut motility (movement of the digestive system that helps process and move food through the gut), aiding in the efficient movement of food and waste through the gastrointestinal tract.
5. Modulation of Gut Microbiome: SCFAs promote the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibit pathogenic strains, maintaining a balanced gut microbial community.
6. Immune Regulation: SCFAs play a role in modulating the immune response in the gut.
7. pH Regulation: SCFAs maintain an acidic environment in the gut, inhibiting the growth of pathogenic (bad) bacteria

The Pivotal Role of Butyrate in Gut Health and IBS
(READ ABOUT IBS)
(READ ABOUT IBS and the MICROBIOME)
Butyrate, a significant short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) found in butter, plays a crucial role in gut health, especially for individuals with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Here are the key roles of butyrate:
1. Energy Source for Gut Cells:
- Butyrate is essential for the function and integrity of intestinal epithelial cells.
- It provides energy for these cells, helping to maintain a healthy gut lining and supporting digestion and absorption.
- Butyrate aids in the regeneration and repair of intestinal cells, vital for overall gut health.
2. Strengthening the Gut Barrier:
- Butyrate enhances tight junction proteins, which strengthens the gut barrier and prevents “leaky gut.”
- This reinforcement ensures harmful substances don’t enter the bloodstream, maintaining effective nutrient absorption and immune function.
3. Anti-inflammatory Properties:
- Butyrate reduces gut inflammation by modulating the immune response.
- It influences the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and reduces pro-inflammatory markers.
- These actions are particularly beneficial for conditions like IBS and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
4. SCFA Production in IBS:
- IBS-related changes in gut microbiome or diet can reduce butyrate levels.
- A low-fiber diet or gut dysbiosis can exacerbate IBS symptoms by reducing butyrate production.
- Restoring butyrate levels through diet or supplementation is crucial for managing IBS.
5. Gut Barrier Dysfunction in IBS:
- Reduced butyrate may increase gut permeability in IBS, leading to “leaky gut.”
- This can trigger an exaggerated immune response and heightened gut sensitivity.
- Enhancing butyrate production helps reinforce the gut barrier and alleviate these symptoms.
6. Reducing Visceral Sensitivity:
- Butyrate may modulate pain perception in the gut, reducing discomfort and pain.
- It influences the nervous system in the gut, potentially lowering visceral sensitivity.
- Increasing butyrate levels through diet (high-fiber foods, prebiotics) or supplementation can improve gut function and reduce IBS symptoms. Eg. Products like MICROBIOMEX® in the DARMBIOMIX SUPPORT formulation are designed to boost butyrate production. (READ ABOUT IT HERE)
Conclusion
Butyrate and other SCFAs are vital for gut health, particularly in managing IBS. Their roles in maintaining barrier integrity, reducing inflammation, and supporting a balanced gut microbiome underscore the importance of a fiber-rich diet. As research advances, the therapeutic potential of butyrate for gut-related disorders becomes increasingly clear, offering promising non-pharmacological treatment options.
Recommended For You
Kristina Cueva
Kristina has always had a passion for understanding diseases and their underlying mechanisms. With a Biomedical sciences background as well as Public Health & Economics, Kristina understands the burdens diseases have on society. This helps her understand the necessary innovations to promote good health which ultimately lower burden of disease.
References:
Blaak EE, Canfora EE, Theis S, Frost G, Groen AK, Mithieux G, Nauta A, Scott K, Stahl B, van Harsselaar J, van Tol R, Vaughan EE, Verbeke K. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef Microbes. 2020 Sep 1;11(5):411-455. doi: 10.3920/BM2020.0057. Epub 2020 Aug 31. PMID: 32865024.
Jian Tan, Craig McKenzie, Maria Potamitis, Alison N. Thorburn, Charles R. Mackay, Laurence Macia, Chapter Three - The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Health and Disease, Editor(s): Frederick W. Alt, Advances in Immunology, Academic Press, Volume 121, 2014, Pages 91-119,
Maurer Sost M, Stevens Y, Salden B, Troost F, Masclee A, Venema K. Citrus Extract High in Flavonoids Beneficially Alters Intestinal Metabolic Responses in Subjects with Features of Metabolic Syndrome. Foods. 2023 Sep 13;12(18):3413. doi: 10.3390/foods12183413. PMID: 37761122; PMCID: PMC10529306.
Parada Venegas D, De la Fuente MK, Landskron G, González MJ, Quera R, Dijkstra G, Harmsen HJM, Faber KN, Hermoso MA. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 11;10:277. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00277. Erratum in: Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 28;10:1486. PMID: 30915065; PMCID: PMC6421268.
Silva YP, Bernardi A, Frozza RL. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jan 31;11:25. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00025. PMID: 32082260; PMCID: PMC7005631.
Xiong RG, Zhou DD, Wu SX, Huang SY, Saimaiti A, Yang ZJ, Shang A, Zhao CN, Gan RY, Li HB. Health Benefits and Side Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods. 2022 Sep 15;11(18):2863. doi: 10.3390/foods11182863. PMID: 36140990; PMCID: PMC9498509.
DISCOVER HOW DARMBIOMIX CAN HELP
Darmbiomix SUPPORT
- Regular price
- €36,95
- Promotional price:
- €36,95
- Regular price
-
€73,90 - Unit price
- per